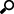Inbound Delivery Agreement Detail
The Inbound Delivery Agreement Detail screen contains the information about a particular delivery agreement. Delivery Agreements can only be created with Suppliers that have an Inbound Partner Agreement with the current Site. The delivery agreement is an agreement together with a particular supplier and concerns a particular product.
Supplier Id / Address - The Id and the Address of the supplier. When you create a new delivery agreement you can choose a supplier from a drop down list.
Customer Manages Agrmts - Indicates that it is the customer that manages the agreement for SMI agreements.
(Status icon) – This icon signals if the delivery agreement is incorrectly configured or out of date with respect to the actual outflow and the parameters in the delivery agreements. For more information click here.
Supplier Name - The name of the supplier.
Supplier – The type of supplier.
Product Id / Variant - The Id and variant of the product. When you create a new delivery agreement you can choose a product (and variant) from a drop down list
Product name - The name of the product.
Supplier’s Product Id / Variant - The Id and Variant of the product in the supplier's order/ERP system or in the supplier's PipeChain.
Supplier Managed Inventory - If this checkbox is checked it means that this is a SMI (VMI) agreement between you and your supplier. For more information click here.
Status - the SMI status of the agreement. It is either Active or Pending change of responsibility.
Last updated - when the SMI status was last changed.
- Used Parameter Group -
Group Id - The used Parameter Group Id
Level - The Used Parameter Group's Level (Server, Business or Site)
Description - The Parameter Group's description
- Calculated Parameter Group -
Group Id - The Calculated Parameter Group Id
Level - The Calculated Parameter Group's Level (Server, Business or Site)
Description - The Parameter Group's description
- Deviation OK -
Acknowledge - A button to acknowledge a deviation between the Used and Calculated Parameter Groups
User - The user name of the user who acknowledged the deviation
Date - The date when the user acknowledged the deviation
Tabs
This tab specifies how the product is to be delivered.
Strategy – this list box displays which replenishment strategy is used in this delivery agreement. There are two strategies, Bucket and Transport.
The Bucket replenishment strategy - Every time a delivery takes place the supplier replenishes as much as possible, within the scope of the agreement. This strategy minimizes the number of shipments needed, while making sure that you always have enough goods. Bucket Strategy is one of PipeChain Supply’s two replenishment strategies. The other one is Transport Strategy (see below). The Transport Strategy is especially suited for big flows.
The Transport replenishment strategy - Minimizes your stock and (may) increase the number of shipments. The "good" thing with this strategy is that it evens out the flow of goods. The "bad" thing is that it increases the number of transports. Shipments are made according to a fixed transport schedule. Each shipment contains just enough goods to last you until the next shipment arrives (+ Safety Time). Therefore a production plan or forecast is required. Transport Strategy is one of PipeChain Supply's two replenishment strategies. The other one is Bucket Strategy (see above)
- Stock Level Control -
Critical Time - The stock level you want your duration meter to turn red at. Should, if used, be considerably less than the Safety Time (or else your meter will never be yellow since the duration meter is turning red directly after is has been yellow). We strongly recommend the usage of Critical Time. If left undefined, the Lead Time will be used as Critical Time. This could be the time it takes 1/ to get goods from another supplier, 2/ to receive an express delivery or 3/ to reschedule the production.
Total Lead Time - Is the sum of Transport Lead Time and Production Lead Time is showing in this field. If editing the Transport Lead Time or Production Lead Time field with a value the Total Lead Time is automatically updated with the same value.
Transport Lead Time - The time it takes from the moment the supplier ships the delivery in PipeChain until it is received, registered and shows up in the customer's stock balance. The Lead Time is only used if the Reception Schedule is of Schedule Type = Reception Days. If it is not, then the Lead Time is only for information purposes.
Production Lead Time - The normal delivery time measured from receipt of order until item is shipped by the seller in the case where the product is not in stock.
Total Lead Time - Is the sum of Transport Lead Time and Production Lead Time. If editing the field directly with a value the Production Lead Time is automatically updated with the same value.
Safety Time - The minimum stock cover time for which you want to have a stock of this product. You decide what the Safety Time should be based on the stability of deliveries and sales, and on the quality of the information covering balance and demand.
Max Time - The maximum stock cover time you want to have stock of a certain product.
Safety Balance - The fixed quantity below which you do not want the stock balance of the product to fall, even if there is no demand of the product. The safety balance overrides the Safety Time. By setting a Safety Balance you make sure that you always have a certain quantity in stock. To make the supply process as smooth as possible, we do not recommend setting a Safety Balance unless it is absolutely necessary.
Max Balance - Is a fixed quantity above which your stock balance of the product must not rise, no matter what the outflow is. The Max Balance overrides the Max Time. Example: a tank that can hold only 1000 liters cannot stock any more liters. We do not recommend setting a Max Balance unless there is a definite physical limit to how much of the product you can store!
Green Balance / Source. The Green Balance is the Balance level under which the Duration Meter should not turn blue. It is aimed to be used for minimizing the number of blue meter due to for instance rounding up to the minimum delivery quantity. The Green Balance can be defined as a value (Fixed) or as the Delivery Unit Quantity or the Multi Unit Quantity. If either if the two last options are used the field will show the current quantity.
- Delivery Quantities -
Min Delivery Quantity - This is the minimum quantity that a delivery can contain. If PipeChain calculates that you need a smaller quantity, the quantity of the delivery will be set to the Min Delivery Quantity.
Multi Unit Quantity - The checkbox is checked if the product is delivered in units of more than one product (e.g. pallet or case). The quantity of the product contained in each multi unit is specified in the field to the right of the checkbox. Delivery quantities are always rounded upwards to the nearest multi unit.
Delivery Unit
- Unit of Measure -
If your supplier have another unit you can use this conversion. When you edit an inbound delivery agreement's unit conversion, you can now use the Delivery Unit Browser when editing the "Supplier's Unit" field. The Delivery Unit you'll find in the Own Bucket Detail under tab Delivery Unit, click here to go to Own Bucket Detail. The browser suggests all Delivery Units defined the product.
Our Unit - Shows the unit that is set up on the product in the own bucket.
Handle as Integer - Shows if the unit is handle as Integer. Taking from the product in own bucket.
Supplier's Unit -
Edit - Press the edit button to edit the Supplier's unit. Choose Supplier's Unit from the list, coming from the Delivery Unit on the product in the own bucket. Define Conversion; choose between the three options. Edit the Conversion factor and you see the Example below.
- Reception Schedule -
Reception Schedule Id - The Id of the Reception Schedule. Choose a Reception Schedule Id in the list. Reception Schedule is important for calculation of suggestion in PipeChain. Click here to see more information about the inbound reception schedule.
Buttons
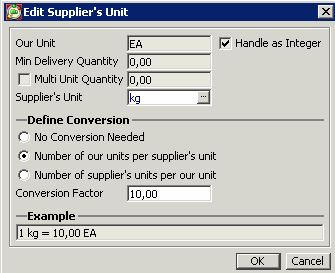
Analyze – when you click this button, PipeChain Supply analyzes the agreement to see if the values are well adapted to your outflow etc. The result is shown in a dialog box as soon as the analysis is complete. This may take a few seconds.
+ Dialog box showing the result of analyzing a delivery agreement.
In this tab, the delivery agreement can be tied to a blanket purchase order An order created by: - PipeChain if it concearns a delivery from a supplier to your PipeChain, or - your purchase/ERP system (or manually by PipeChain) if it concearns a delivery from a supplier to your PipeChain, or - the customer's purchase/ERP system, if it concearns a delivery from your PipeChain to a customer. in your purchasing system. The information in this tab can either be entered manually via custom-made Microsoft Excel sheets provided by PipeChain AB, or transferred automatically from the purchasing system.
Blanket Order The blanket order is a reference used to identify the customer's purchase order.The blanket order reference can be used to make goods receipts. The blanket orderreference is normally created in the customer's order system and sent to PipeChain,or entered manually. – if Not Used is selected, no blanket purchase order is used, even if one is specified in the list of blanket orders. If Scheduled is selected, a blanket order is used. It is specified in the list below.
Valid From Date – the date from which the blanket order is valid. Out of all blanket orders in the list, the one with the latest “Valid From” date is the one which is valid. When the supplier’s PipeChain Supply creates a delivery suggestion, it uses the blanket order with the nearest “Valid From” date that is in the past.
Purchase Order Id – the ID of the blanket order in your purchase system.
Purchase Order Line Id – the line number of the blanket order in your purchase system.
In the three Order Text fields in the Order Data tab, you can enter data, such as order type The order type in PipeChain is either Replenishment Order, Sales Order or Purchase Order. The orders are either outbound from or inbound to this PipeChain Supply., cost center etc that is needed by your purchasing system and/or the supplier’s order system, if the supplier is not using their own PipeChain Supply.
Whenever a new inbound delivery of this product is advised to you from this supplier via a data exchange, the information you have entered in the Order Text tab is transferred to your purchasing system together with the delivery advice.
Whenever a new suggestion is sent to the purchasing system the information you have entered in the Order Text tab is transferred to your purchasing system together with the delivery advice.
Whenever a request is sent to the supplier the information you have entered in the Order Text tab is transferred to your purchasing system together with the delivery advice
In the nine Order Boolean, Decimal and Integer fields in the Order Data tab, you can enter data, such as order type The order type in PipeChain is either Replenishment Order, Sales Order or Purchase Order. The orders are either outbound from or inbound to this PipeChain Supply., cost center etc that is needed by your purchasing system and/or the supplier’s order system, if the supplier is not using their own PipeChain Supply. These fields are not sent in the standard Order transactions but can be used for integration via converters.
The Partial Bucket tab is used if the responsibility for supplying the product in question is shared between more than one supplier. It shows you the current status of this supplier’s share of replenishing your stock of this product.
(You define each supplier’s share of the responsibility for delivering a product in the Delivery Agreement tab in the Own Bucket Detail screen.
Each share is treated as a separate “product bucket”. What you see in the Partial Bucket for the supplier is what the supplier sees when he looks in “your” Customer Bucket in his PipeChain Supply. In other words, only you can see that a supplier is supplying only a share of the total product stock. The supplier cannot see that he is one of several suppliers of this product.
The above are similar to features in the Own Bucket Detail screen. You might want to check the description of that screen also.
(Duration Meter) – a graphical presentation of the duration. For an explanation of how to read the Duration Meter, This Duration Meter only concerns the responsibility, i.e. the replenishment share Customer might choose several suppliers for one product (multiple sourcing). Replenishment share is the percentage that each supplier is given by its customer. Each share is treated as a separate "product bucket". Only the customer can see that a supplier is supplying only a share of the total product stock. The supplier cannot see that he is one of several suppliers of this product., of the supplier in question.
Duration – the time until this supplier’s share of your stock of the product (or Product Variant) runs out. This value is based on the supplier’s replenishment share (7), your balance of the product and your outflow of the product.
Stock In Transit – the duration (see above) of the quantity of this product that is on its way from this supplier (i.e. deliveries that have been confirmed).The cover time of the stock in transit of this product (i.e. confirmed and shipped deliveries).
Partial Balance – the quantity received from this supplier minus the supplier’s share of the outflow of this product.
Shortage - the supplier’s share of the total shortage of the product (for an explanation of what shortage means in PipeChain Supply, see the description of the Bucket tab in the Own Bucket Detail screen.
Partial Virtual Balance – the quantity of this supplier’s share of your stock of this product and inbound deliveries that you have not yet received from this supplier – minus this supplier’s share of the outflow of the product and shortage.
-----
Replenishment Share – this field contains the supplier’s share (in percent) of the responsibility for replenishing your stock of the product in question. (You define this share in the Delivery Agreement tab in the Own Bucket Detail screen). If there is a * next to the Replenishment Share, it means that the share is going to be changed in the future. Customer might choose several suppliers for one product (multiple sourcing). Replenishment share is the percentage that each supplier is given by its customer. Each share is treated as a separate "product bucket". Only the customer can see that a supplier is supplying only a share of the total product stock. The supplier cannot see that he is one of several suppliers of this product.
Replenishment Constraints - in this field, you specify if there is an upper or lower limit to the quantity this supplier can or should supply during a withdrawal period (11). You can choose maximum, minimum, or none.
Quantity – the maximum or minimum quantity that the supplier can supply per day.
-----
Withdrawal Day – the quantity that has been withdrawn from this supplier’s share of your stock of this product (or this Product Variant) today.
Withdrawal Period – the quantity that has been withdrawn from this supplier’s part of your stock of this product (or this Product Variant) during this period. The withdrawal period can be either one day (in which case the value here is the same as in No. 10) or one week. The period length is set in the Delivery Agreement tab of the Own Bucket Detail screen.
Buttons
Inventory Chart – if you click on this button, you open an Inventory Chart for this Partial Bucket.
Generate Delivery Suggestions – if you click on this button, a new delivery suggestion will be created for this supplier and product.
The Partial Flow Model tab shows the Flow Model graph that applies to this supplier, if the supplier is supplying only part of your stock of a product. It is used only if the following are true:
The responsibility for supplying the product in question is shared between more than one supplier
You have an Own Flow Model for this product
and one of the following is true:
The period type of the Own Flow Model is “Sales Forecast” and
“Production Plan Daily” (this is explained in the section about the Own Flow Model Detail screen), or
The supplier has a replenishment constraint for his share of your stock, i.e. a maximum or a minimum amount that he can deliver.
If the above conditions are not met, but you have an Own Flow Model for the product, the values of the Own Flow Model will apply instead.
The layout and function of this tab is similar to that of the Flow Model Graph tab in the Own Flow Model Detail screen. Level – you can choose if you want to view the outflow per day, per week or per month. By selecting Week or Month a panel becomes visible (see image below). The panel shows the outflow for each day the week you have highlighted. You can see the total outflow of the week or month in the Outflow field.
If you select Day you see the daily outflow to the left in the Partial Flow Model tab.
+ The Partial Flow Periods Tab
This tab shows the Flow Periods of the Partial Flow Model, if the supplier is supplying only part of your stock of a product. If no Flow Model is defined for the product, the Flow Meter value is shown.
The layout and function of this tab is similar to that of the Flow Periods tab in the Own Flow Model Detail screen.
+ The Delivery Suggestion Parameters
Set delivery to status Forecast - determines if the suggestion generation should create delivery suggestions with status Forecast instead of with status Suggestion. Delivery suggestions in status Forecast can not be used to create deliveries or orders by the supplier.
- Sending of Suggestions -
Send Delivery Suggestions - Default value is "As Specified in the Own Business Screen". If this alterative is used the Own Business sending strategy will be displayed in the field to the right. You can override this central sending strategy by changing the drop-down box.
Auto send lower limit - If used suggestion below this limit will not automatically be sent to the order system by PipeChain.
Auto send upper limit - If used suggestion above this limit will not automatically be sent to the order system by PipeChain.
Suggestions outside
the above limits will be set to the status On Hold. If a suggestion
is On Hold and is within the Confirmation Margin it will not get sent
to the order system in the sending process. Instead a message will
be produced and put into the message log.
Suggestions that are On Hold will not be shown in the Flow Model type
"From Outbound Deliveries".
-Backlog-
Compensate for Backlog During Lead Time - If Flow Meter or Sales Forecast (and no other strategy is used) is used, and there is an expected backlog in the future – before the next reception – PipeChain can either takes this into account or not. The box should be checked to compensate if back orders are normally used in a situation like this. Do not check the box if sales of this product is lost at stockouts.
- Confirmation Margin -
Strategy for Confirmation Margin - The Confirmation Margin can be supplied on Partner agreement level or Delivery Agreement level.
The limit date for confirmation called Delivery Preparation Time (DPT) are now calculated by subtracting the sum of production lead time and confirmation margin from the delivery shipment time (ST), The suppliers calendar is used when calculating DPT. The DPT affects the severity (Color) on Shipment Time and when deliveries are sent automatically to ERP system. The attribute Lead Time is now renamed to Transport Lead Time (TLT). A production Time (PT) is also displayed in deliveries and suggestion screens but only if production lead time is greater than 0.
Lead Times: CM PLT TLT
--------------|----------------|-------------------|--------------------|
DPT PT ST RT (ReceptionTime)
Reports- Using with Management Dashboard. Check the checkbox means reports excluding from Service Level and Delivery Precision Reports
Use Consignment Stock - A product can be activated as a consignment product. If checking this checkbox will enable the Consignment tab in the own Bucket Detail screen and the Inbound Delivery Agreement Detail screen. Transaction CS04 Inventory Report is extended to also report consignment consumption. Consumption lines stored in Inventory Activity can be forwarded to the supplier in a transaction PW55 Consumption Report. The scheduling of sending PW55 is configured in screen Inbound Partner Agreement tab Advanced. The scheduling is done by a calendar, the report will be sent on all open days in the calendar and the time is determined by a new field. A supplier can have both consignment products and none consignment products.
A product can have several consignment suppliers it can also have both consignment suppliers and none consignment suppliers.
- Addresses -
It is possible to set the Delivery Recipient and Goods Recipient belonging to a product.
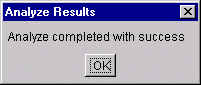
Each PriceRange defines a Minimum Quantity and/or Maximum Quantity and a Price Per Unit.
Each agreement may have one or more price ranges (but they may not overlap.
Price per UnitPriceBase. The price displayed to the user will be the Price Per UnitPriceBase + the UnitPriceBase
Number of Units that the Price is for. Default is 1 Unit.
(A special screen with Price Ranges will be available to make manual maintenance more convenient.)
In the Consignment Tab you find information about the Consignment consumption lines displayed for this product. The Consignment Tab is enable if activated as a consignment product in check box "Use Consignment Stock" in Advanced Tab.
Transaction CS04 Inventory Report is extended to also report consignment consumption. Consumption lines stored in Inventory Activity can be forwarded to the supplier in a transaction PW55 Consumption Report. The scheduling of sending PW55 is configured in screen Inbound Partner Agreement tab Advanced. The scheduling is done by a calendar, the report will be sent on all open days in the calendar and the time is determined by a new field. A supplier can have both consignment products and none consignment products.
A product can have several consignment suppliers it can also have both consignment suppliers and none consignment suppliers.
For a consignment product is all balance updates logged in the InvActivity table. There are 5 types of activities
1. Consignment Consumption
2. Consignment Correction
3. Delivery Receipt
4. Cancel Delivery Receipt
5. Inventory Adjustment
It possible to correct Consignment Balance with a button "Correct Consignment Balance" in a new tab Consignment in screen Inbound Delivery Agreement.
It possible to send PW55 Consumption Report manually for a certain product. This is done by using the button "Send Consumption Report".
Requirements for Consignment in PipeChain is that the ERP system at customer side must be able to send consumption report for each consignment supplier and that the supplier must be able to register a ’warehouse’ (Location Id) in his system to represent each customer’s consignment stock.
When Registration
of a consignment product (done in the Inbound
Delivery Detail screen)they extended with Consignment Info Possible
to enter batch number etc. (default is delivery Id)
Location Id: Possible to enter Warehouse id
example
In the Terms of Delivery tab it is possible to set the terms of delivery on product level.
Terms of Delivery - Choose From Partner Agreement or choose from Delivery Agreement. Choosing From Partner Agreement the settings inherits from Partner Agreement and are not editable.
Settings - If choosing From Deliver Agreement in Terms of Delivery the settings are editable.
Use Until Reception if using Reception Time in the process. Use Until Shipment if using with Shipment Time. Use According to Terms of the Delivery Codes if using terms of Delivery code in the process.
Codes -
Set the Terms of Payment Code, Terms of Delivery Code and Mode of Delivery Code if using VMI flow.

if there is documents using to the product it will be shown here.
Buttons
Set Inventory Responsible - To read more about this click here.
Change of Inbound Agreement between SMI and non-SMI
If the Supplier is of the Supplier Type "Has WebAccess to This PipeChain Supply" it is possible to change between SMI and non-SMI responsibility. The change can be initiated by the Customer for non-SMI agreements and by both parties for SMI agreements. The other party can accept the (suggested) change and can also reject the (suggested) change.
To initiate the change from the Customer
The customer user goes
to the Inbound Delivery Agreement screen and selects / clicks "Set
Inventory Responsible". In the dialog the customer user chooses
"Yes".
The agreement now shows up in the WebAccess as red. Also a Message
is created in the Message Log and can be sent to the Supplier. The
supplier web user goes to the Outbound Delivery Agreement Overview
screen. If the agreement is not visible the supplier web user may
sort on the column "SMI Status" to see the agreements that
needs to be changed. The supplier web user goes to the Outbound Delivery
Agreement Detail screen for the Agreement and clicks on the button
"Set Inventory Responsible" and then clicks "Yes".
To initiate the change from the Supplier
The supplier web user
goes to the Outbound Delivery Agreement Detail screen and clicks "Set
Inventory Responsible". In the dialog the supplier web user chooses
"Yes".
The agreement now shows up in the Supply Standard client as red. Also
a Message is created in the Message Log and can be sent to the Customer.
The customer user goes to the Inbound Delivery Agreement screen. If
the agreement is not visible the customer user may sort on the column
"SMI Status" to see the agreements that needs to be changed.
The customer user selects / clicks "Set Inventory Responsible"
and then clicks "Yes".
Links
Partner Agreement - if you click on this link, you open the Inbound Partner Agreement Detail screen, where you can view and edit the partner agreement for this supplier.